|
AQUACULTURE
|
|
|
CHINA:
Cultivating emergent aquatic plants in floating containers. Apart from fish and shrimp, some aquaculture undertakings, such as seaweed and filter-feeding bivalve mollusks like oysters, clams, mussels and scallops, are relatively benign and even environmentally restorative. Filter-feeders filter pollutants as well as nutrients from the water, improving water quality. Seaweeds extract nutrients such as inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus directly from the water, and filter-feeding mollusks can extract nutrients as they feed on particulates, such as phytoplankton and detritus.
One of the most pressing concerns at the moment the world over is the growing plastic content in our oceans that is getting into the farmed and wild fish food chain, including ocean based fish farming operations. A report in March of 2015 from the NCEAS in California, puts waste levels as high as 12 million tons, with a mean of 8 million tons. The real issue is that this is not being tackled by anyone on an urgent basis, save for a robotic ocean plastic recovery project in the United Kingdom, that is at an early stage in development and constantly on the look out for funding to go from a feasibility study to the build of a fully functional prototype SeaVax. To date (14-1-17) the company developing the technology is licensed to work on the concept, but may have to pass the IP torch to a charity with similar objectives that is more grant friendly, where their present funding comes to an end in April 2017 and the company has sustained research losses that they cannot afford to escalate. We will report on this further as we hear any news. We know that a European consortium is looking to utilize SeaVax for eventual clean up operations in the Mediterranean.
ROBOCULTURE: Robotic boats and ships such as the RiverVax and SeaVax concepts as developed by Bluebird Marine Systems, now supported by the Cleaner Oceans Foundation, may be technology coming to the rescue for sustainable blue growth, where man had been steadily fouling his own doorstep.
Onshore recirculating aquaculture systems, facilities using polyculture techniques, and properly sited facilities (for example, offshore areas with strong currents) are examples of ways to manage negative environmental effects. Banning plastic for packaging that wild and farmed fish ingest would have an immediate and beneficial effect on fish health, but this is not going to happen.
WHAT IS AQUACULTURE ?
Aquaculture, also known as
aqua-farming, is the farming of
fish, crustaceans, molluscs, aquatic plants, algae, and other aquatic organisms. Aquaculture involves cultivating freshwater and saltwater populations under controlled conditions, and can be contrasted with commercial
fishing, which is the harvesting of wild fish. Mariculture refers to aquaculture practiced in marine environments and in underwater habitats.
INEFFICIENT
Some carnivorous and omnivorous farmed fish species are fed wild forage fish. Although carnivorous farmed fish represented only 13 percent of aquaculture production by weight in 2000, they represented 34 percent of aquaculture production by
value.
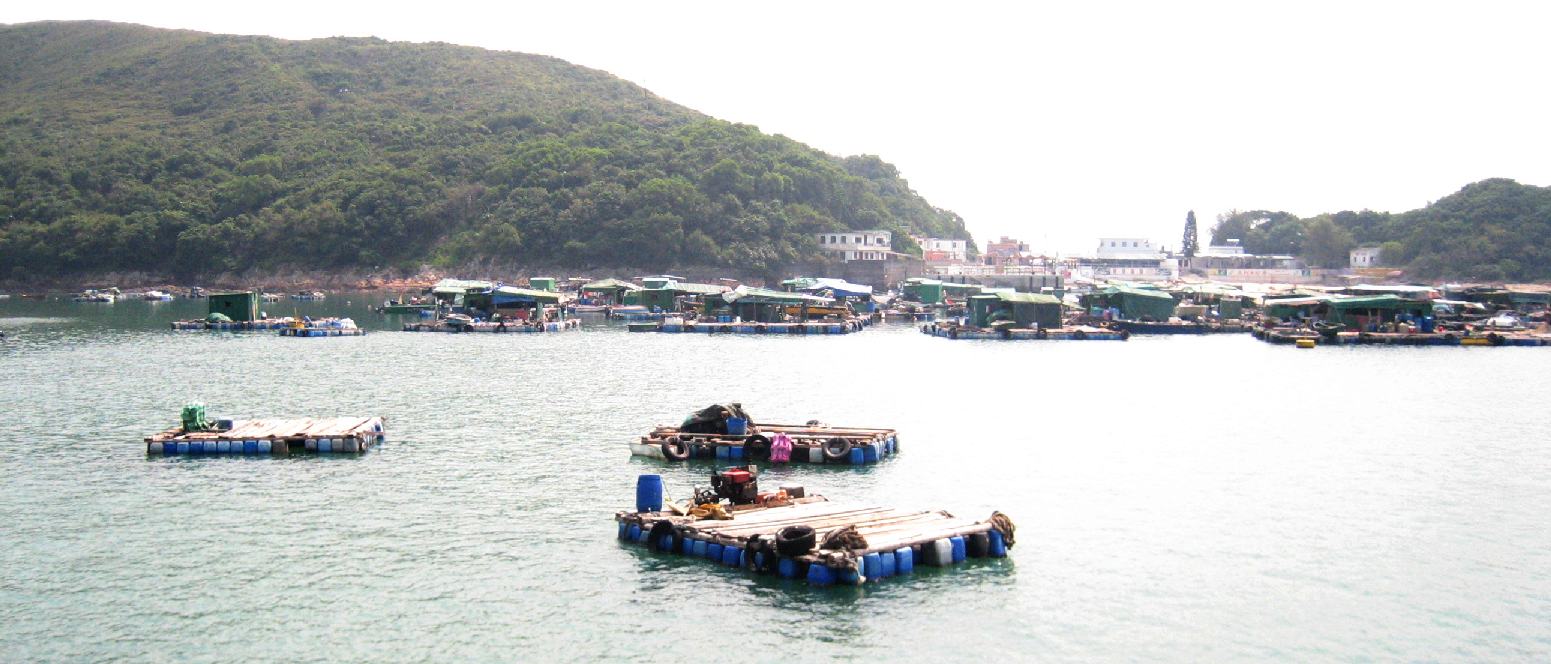
HONG KONG: Mariculture off High Island, Hong Kong. Global wild fisheries are in decline, with valuable habitat such as estuaries in critical condition. The aquaculture or farming of piscivorous fish, like salmon, does not help the problem because they need to eat products from other fish, such as fish meal and fish oil. Studies have shown that salmon farming has major negative impacts on wild salmon, as well as the forage fish that need to be caught to feed them. Fish that are higher on the food chain are less efficient sources of food energy.
Recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS) recycle water by circulating it through filters to remove fish waste and food and then recirculating it back into the tanks. This saves water and the waste gathered can be used in compost or, in some cases, could even be treated and used on land. While RAS was developed with freshwater fish in mind, scientist associated with the Agricultural Research Service have found a way to rear saltwater fish using RAS in low-salinity waters. Although saltwater fish are raised in off-shore cages or caught with nets in water that typically has a salinity of 35 parts per thousand (ppt), scientists were able to produce healthy pompano, a saltwater fish, in tanks with a salinity of only 5 ppt. Commercializing low-salinity RAS are predicted to have positive environmental and economical effects. Unwanted nutrients from the fish food would not be added to the ocean and the risk of transmitting diseases between wild and farm-raised fish would greatly be reduced. The price of expensive saltwater fish, such as the pompano and combia used in the experiments, would be reduced. However, before any of this can be done researchers must study every aspect of the fish's lifecycle, including the amount of ammonia and nitrate the fish will tolerate in the water, what to feed the fish during each stage of its lifecycle, the stocking rate that will produce the healthiest fish, etc.
BACKGROUND
Harvest stagnation in wild fisheries and overexploitation of popular marine species, combined with a growing demand for high-quality protein, encouraged aquaculturists to domesticate other marine species. At the outset of modern aquaculture, many were optimistic that a
"Blue
Revolution" could take place in aquaculture, just as the Green Revolution of the 20th century had revolutionized agriculture. Although land animals had long been domesticated, most seafood species were still caught from the wild. Concerned about the impact of growing demand for seafood on the world's oceans, prominent ocean explorer Jacques Cousteau wrote in 1973: "With earth’s burgeoning human populations to feed, we must turn to the sea with new understanding and new technology.”
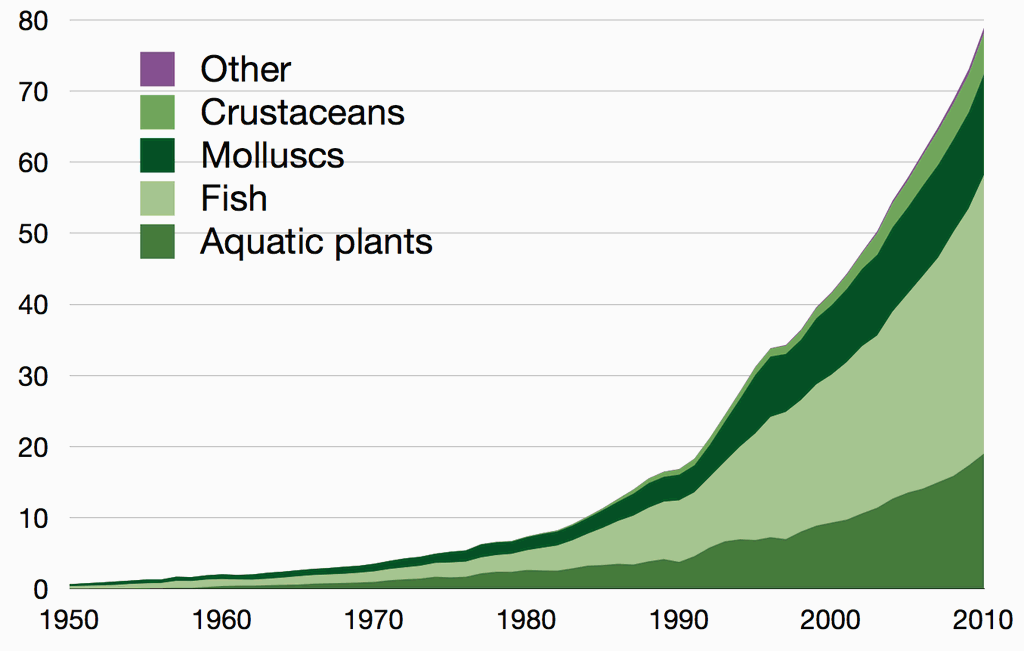
Global aquaculture production in million tonnes, 1950–2010, as reported by the FAO
FISH FARMING
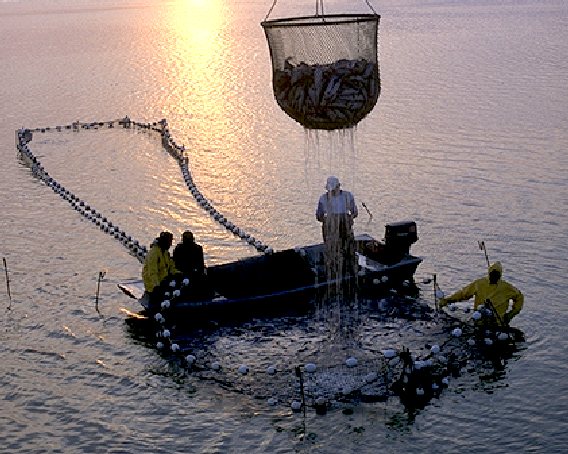
The farming of fish is the most common form of aquaculture. It involves raising fish commercially in tanks, ponds, or ocean enclosures, usually for food. A facility that releases juvenile fish into the wild for recreational fishing or to supplement a species' natural numbers is generally referred to as a fish hatchery. Worldwide, the most important fish species used in fish farming are, in order, carp, salmon, tilapia, and catfish.
Some 16 countries now use geothermal
energy for aquaculture, including China, Israel, and the United States. In California, for example, 15 fish farms produce tilapia, bass, and catfish with warm water from underground. This warmer water enables fish to grow all year round and mature more quickly. Collectively these California farms produce 4.5 million kilograms of fish each year.
ROBOCULTURE: Robotic boa
Manuel Maqueda, the co-founder of the Plastic Pollution Coalition is quoted as saying that we're stuck. We understand plastic pollution issues, but we don't have the solutions. The voice of the Earth is not being heard. He was driven to seek plastic pollution justice after a conversation with oceanographer Captain Charles Moore, who is also the founder of the Algita Marine Research Foundation. Moore shared with him what appeared to be a bag of sand which, Maqueda realized, was a bag of minute pieces of plastic. Moore told Maqueda, "that's the beaches of the future…. It's the global warming 30 years ago coming to us now.” Maqueda wanted to take action, to solve environmental issues that were being ignored. After research and collaboration with Google Earth, he gathered a group of individuals with a shared interest and passion for plastic pollution justice to meet at the Google Headquarters. Together they addressed "what this problem is, what the solutions are, and what the solutions are not." One practical solution is to adapt a fleet of solar powered drones to clean up the oceans. The NOC were approached in 2013 with such a suggestion and got no reply. The Technology Strategy Board rejected an application for funding in May of 2013. Bluebird Marine Systems has a published patent that covers a system for such a clean up, but needs financial support for the research needed to make it happen.
ACIDIFICATION - ADRIATIC - ARCTIC - ATLANTIC - BALTIC - BERING - CARIBBEAN - CORAL - EAST CHINA ENGLISH CH - GULF MEXICO - INDIAN - MEDITERRANEAN - NORTH SEA - PACIFIC - PERSIAN GULF - SEA JAPAN STH
CHINA - PLASTIC
- PLASTIC
OCEANS - SEA
LEVEL RISE
LINKS:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aquaculture EU Aquaculture Conference 2016 speakers Events Scottish Enterprise Silverbear http://euaquacultureconference2016.eu/speakers.html https://events.scottish-enterprise.com/events/ClientApps/Silverbear.Web.EDMS/public/default.aspx?tabid=37&id=300400&orgId=1
|
|
|
This website is Copyright © 2017 Cleaner Oceans Foundation an educational charity working hard for world peace. The bird logos and names SeaVax and AmphiMax are trademarks. All rights reserved. All other trademarks are hereby acknowledged.
|