|
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning 93,030 square
kilometres (35,920 sq mi) of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and Slovenia to the southwest, and Austria to the west. Hungary has a population of 9.6 million, mostly ethnic Hungarians and a significant Romani minority. Hungarian is the official language, and Budapest is the country's capital and largest city.
Prior to the foundation of the Hungarian state, various peoples settled in the territory of present-day Hungary, most notably the Celts, Romans, Huns, Germanic peoples, Avars and Slavs. The Principality of Hungary was established in the late 9th century by Álmos and his son Árpád through the conquest of the Carpathian Basin. King Stephen I ascended the throne in 1000, converting his realm to a Christian kingdom. The medieval Kingdom of Hungary was a European power, reaching its height in the 14th-15th century. After a long period of Ottoman wars, Hungary's forces were defeated at the Battle of Mohács and its capital was captured in 1541, opening roughly a 150 years long period when the country was divided into three parts: Royal Hungary loyal to the Habsburgs, Ottoman Hungary and the largely independent Principality of Transylvania. The reunited Hungary came under Habsburg rule at the turn of the 18th century, fighting a war of independence in 1703–1711, and a war of independence in 1848–1849 until a compromise allowed the formation of the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy in 1867, a major power into the early 20th century. Austria-Hungary collapsed after World War I, and the subsequent Treaty of Trianon in 1920 established Hungary's current borders, resulting in the loss of 71% of its historical territory, 58% of its population, and 32% of its ethnic Hungarians.
In the interwar period, after initial turmoil, Miklós Horthy ascended as a determining politician, representing the monarchy as regent in place of the Habsburgs. Hungary joined the Axis powers in
World War II, suffering significant damage and casualties. As a result, the Hungarian People's Republic was established as a satellite state of the Soviet Union. Following the failed 1956 revolution, Hungary became a comparatively freer, though still repressed, member of the Eastern Bloc. In 1989, concurrently with the Revolutions of 1989, Hungary peacefully transitioned into a democratic parliamentary republic, joining the European Union in 2004 and being part of the Schengen Area since 2007.
Hungary is a high-income economy with universal health care and tuition-free secondary education. Hungary has a long history of significant contributions to arts, music, literature, sports, science and technology. It is a popular tourist destination in Europe, drawing 24.5 million international tourists in 2019. It is a member of numerous international organisations, including the Council of Europe,
NATO, United
Nations, World Health
Organization, World Trade Organization, World
Bank, Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, and the Visegrád Group.
POST SECOND WORLD WAR
Following the defeat of Nazi Germany, Hungary became a satellite state of the Soviet Union. The Soviet leadership selected Mátyás Rákosi to front the Stalinisation of the country, and Rákosi de facto ruled Hungary from 1949 to 1956. His government's policies of militarisation, industrialisation, collectivisation, and war compensation led to a severe decline in living standards. In imitation of Stalin's KGB, the Rákosi government established a secret political police, the ÁVH, to enforce the regime; approximately 350,000 officials and intellectuals were imprisoned or executed from 1948 to 1956. Many freethinkers, democrats, and Horthy-era dignitaries were secretly arrested and extrajudicially interned in domestic and foreign gulags. Some 600,000 Hungarians were deported to Soviet labour camps, where at least 200,000 died.
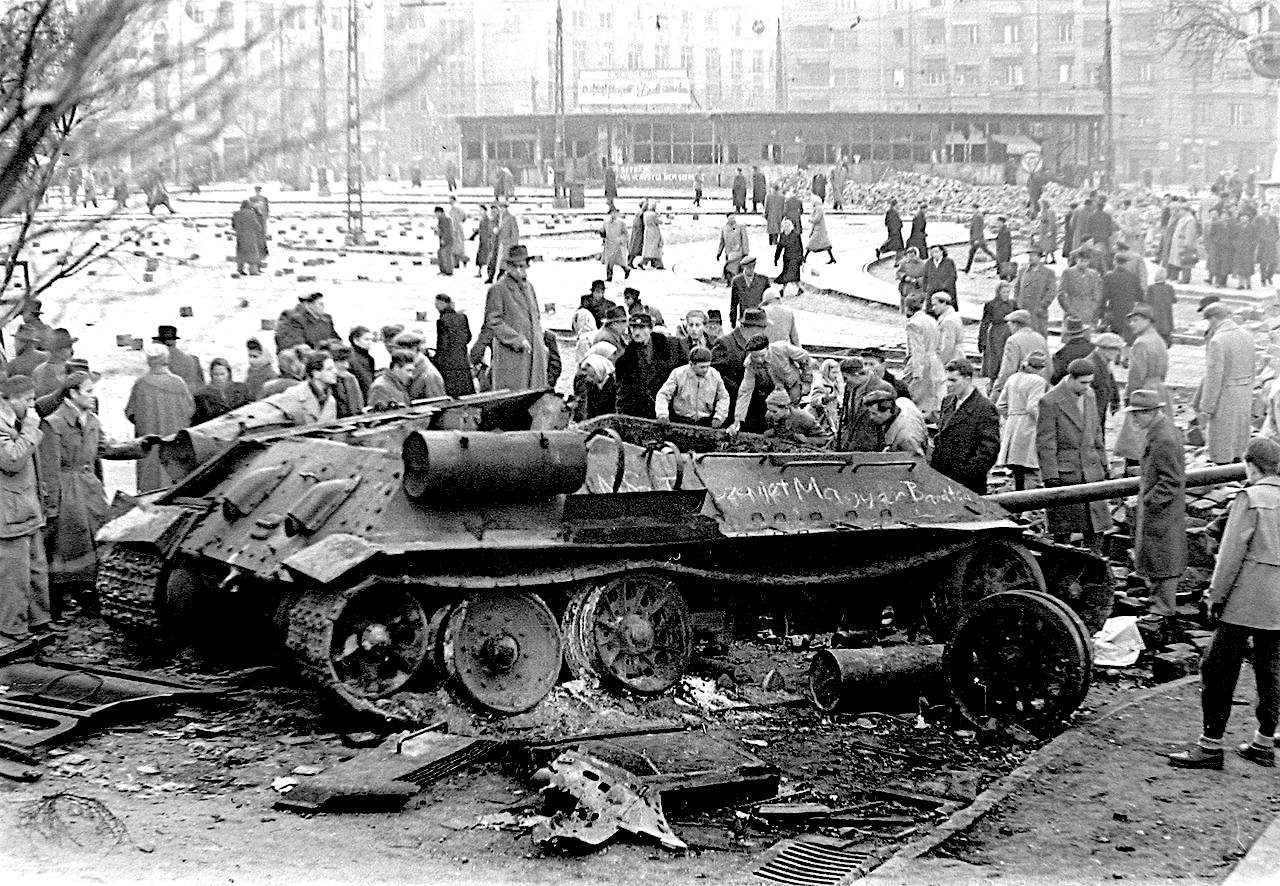
After Stalin's death in 1953, the Soviet Union pursued a programme of de-Stalinisation that was inimical to Rákosi, leading to his deposition. The following political cooling saw the ascent of Imre Nagy to the premiership. Nagy promised market liberalisation and political openness. Rákosi eventually managed to discredit Nagy and replace him with the more hard-line Ernő Gerő. Hungary joined the Warsaw Pact in May 1955, as societal dissatisfaction with the regime swelled. Following the firing on peaceful demonstrations by Soviet soldiers and secret police, and rallies throughout the country on 23 October 1956, protesters took to the streets in Budapest, initiating the 1956 Revolution.
In an effort to quell the chaos, Nagy returned as premier, promised free elections, and took Hungary out of the Warsaw Pact. The violence nonetheless continued as revolutionary militias sprung up against the Soviet Army and the ÁVH; the roughly 3,000-strong resistance fought Soviet tanks using Molotov cocktails and machine-pistols. Though the preponderance of the Soviets was immense, they suffered heavy losses, and by 30 October 1956, most Soviet troops had withdrawn from Budapest to garrison the countryside. For a time, the Soviet leadership was unsure how to respond but eventually decided to intervene to prevent a destabilisation of the Soviet bloc. On 4 November, reinforcements of more than 150,000 troops and 2,500 tanks entered the country from the Soviet Union. Nearly 20,000 Hungarians were killed resisting the intervention, while an additional 21,600 were imprisoned afterward for political reasons. Some 13,000 were interned and 230 brought to trial and executed. Nagy was secretly tried, found guilty, sentenced to death, and executed by hanging in June 1958. Because borders were briefly opened, nearly a quarter of a million people fled the country by the time the revolution was suppressed.
After a second, briefer period of Soviet military occupation, János Kádár, Nagy's former minister of state, was chosen by the Soviet leadership to head the new government and chair the new ruling Socialist Workers' Party. Kádár quickly normalised the situation. In 1963, the government granted a general amnesty. Kádár proclaimed a new policy line, according to which the people were no longer compelled to profess loyalty to the party if they tacitly accepted the socialist regime as a fact of life. Kádár introduced new planning priorities in the economy, such as allowing farmers significant plots of private land within the collective farm system (háztáji gazdálkodás). The living standard rose as consumer goods and food production took precedence over military production, which was reduced to one-tenth of prerevolutionary levels.
In 1968, the New Economic Mechanism introduced free-market elements into the socialist command economy. From the 1960s through the late 1980s, Hungary was often referred to as "the happiest barrack" within the Eastern bloc. During the latter part of the Cold War Hungary's GDP per capita was fourth only to East Germany, Czechoslovakia, and the Soviet Union. As a result of this relatively high standard of living, a more liberalised economy, a less censored press, and less restricted travel rights, Hungary was generally considered one of the more liberal countries in which to live in Central Europe during communism. In 1980, Hungary sent a Cosmonaut into space as part of the Interkosmos. The first Hungarian astronaut was Bertalan Farkas. Hungary became the seventh nation to be represented in space by him. In the 1980s, however, living standards steeply declined again because of a worldwide recession to which communism was unable to respond. By the time Kádár died in 1989, the Soviet Union was in steep decline and a younger generation of reformists saw liberalisation as the solution to economic and social issues.

FROM COMMUNISM TO CAPITALISM
Hungary's transition from communism to capitalism (rendszerváltás, "regime change") was peaceful and prompted by economic stagnation, domestic political pressure, and changing relations with other Warsaw Pact countries. Although the Hungarian Socialist Workers' Party began Round Table Talks with various opposition groups in March 1989, the reburial of Imre Nagy as a revolutionary martyr that June is widely considered the symbolic end of communism in Hungary. Free elections were held in May 1990, and the Hungarian Democratic Forum, a major conservative opposition group, was elected to the head of a coalition government. József Antall became the first democratically elected prime minister since
World War
II.
With the removal of state subsidies and rapid privatisation in 1991, Hungary was affected by a severe economic recession. The Antall government's austerity measures proved unpopular, and the Communist Party's legal and political heir, the Socialist Party, won the subsequent 1994 elections. This abrupt shift in the political landscape was repeated in 1998 and 2002; in each electoral cycle, the governing party was ousted and the erstwhile opposition elected. Like most other post-communist European states, however, Hungary broadly pursued an integrationist agenda, joining NATO in 1999 and the European Union in 2004. As a NATO member, Hungary was involved in the Yugoslav Wars.
In 2006, major nationwide protests erupted after it was revealed that Prime Minister Ferenc Gyurcsány had claimed in a closed-door speech that his party "lied" to win the recent elections. The popularity of left-wing parties plummeted in the ensuing political upheaval, and in 2010, Viktor Orbán's national-conservative Fidesz party was elected to a parliamentary supermajority. The legislature consequently approved a new constitution, among other sweeping governmental and legal changes including the establishment of new parliamentary constituencies, decreasing the number of parliamentarians, and shifting to single-round parliamentary elections.
During the 2015 migrant crisis, the government built a border barrier on the Hungarian-Croatian and Hungarian-Serbian borders to prevent illegal migration. The Hungarian government also criticised the official European Union policy for not dissuading migrants from entering Europe. From 17 October 2015 onward, thousands of migrants were diverted daily to Slovenia instead. Migration became a key issue in the 2018 parliamentary elections, which Fidesz won with a supermajority. In the late 2010s, Orbán's government came under increased international scrutiny over alleged rule-of-law violations. In 2018, the European Parliament voted to act against Hungary under the terms of Article 7 of the Treaty on European Union. Hungary has and continues to dispute these allegations.
The coronavirus pandemic significantly impacted Hungary. The first cases were announced in Hungary on 4 March 2020; on 18 March 2020, surgeon general Cecília Müller announced that the virus had spread to every part of the country. In February 2021, after Hungary became the first EU country and one of the first in the former Warsaw Pact to authorize Russian and Chinese vaccines, it briefly enjoyed one of the highest vaccination rates in Europe.
Relations between Hungary and its Western partners have strained, because Orbán's government has maintained relations with Russia despite sanctions against Russia after the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine. Hungary's leadership has received criticism from several organizations accusing it of becoming a hybrid regime, and regarding LGBT rights in Hungary.

ECONOMY
Hungary is an OECD high-income mixed economy with a very high
human development index and skilled labour force with the 16th lowest income inequality in the world. Furthermore, it is the 9th most complex economy according to the Economic Complexity Index. The economy is the 57th-largest in the world (out of 188 countries measured by IMF) with $265.037 billion output and ranks 49th in the world in terms of GDP per capita by purchasing power parity. Hungary is an export-oriented market economy with a heavy emphasis on foreign trade, thus the country is the 36th largest export economy in the world. The country has more than $100 billion export in 2015 with high, $9.003
billion trade surplus, of which 79% went to the EU and 21% was extra-EU trade. Hungary has a more than 80% privately owned economy with 39.1% overall taxation, which provides the basis for the country's welfare economy. On the expenditure side, household consumption is the main component of GDP and accounts for 50% of its total use, followed by gross fixed capital formation with 22% and government expenditure with 20%. Hungary continues to be one of the leading nations for attracting foreign direct investment (FDI) in Central and Eastern Europe; the inward FDI in the country was $119.8 billion in 2015, while investing more than $50 billion abroad.
As of 2015, the key trading partners were Germany, Austria, Romania, Slovakia, France, Italy, Poland and Czech Republic. Major industries include food processing, pharmaceuticals, motor vehicles, information technology, chemicals, metallurgy, machinery, electrical goods, and tourism (with 12.1 million international tourists in 2014). Hungary is the largest electronics producer in Central and Eastern Europe.
Electronics manufacturing and research are among the main drivers of innovation and economic growth in the country. In the past 20 years Hungary has also grown into a major centre for mobile technology, information security, and related hardware research. The employment rate was 68.3% in 2017; the employment structure shows the characteristics of post-industrial economies, 63.2% of employed workforce work in service sector, the industry contributed by 29.7%, while agriculture with 7.1%. Unemployment rate was 4.1% in 2017, down from 11% during the financial crisis of 2007–2008. Hungary is part of the European single market which represents more than 508 million consumers. Several domestic commercial policies are determined by agreements among European Union members and by EU legislation.
Large Hungarian companies are included in the BUX, the stock market index listed on Budapest
Stock
Exchange. Well-known companies include the Fortune Global 500 firm MOL Group, the OTP Bank, Gedeon Richter Plc., Magyar Telekom, CIG Pannonia, FHB Bank, Zwack Unicum and more. Besides this Hungary has a large portion of specialised small and medium enterprise, for example a significant number of automotive suppliers and technology start ups among others.
Budapest is the financial and business capital, classified as an Alpha world city in the study by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network. Budapest is the primate city of Hungary regarding business and economy, accounting for 39% of the national income, the city has a gross metropolitan product more than $100 billion in 2015, making it one of the largest regional economies in the European Union. Budapest is also among the Top 100 GDP performing cities in the world, measured by PricewaterhouseCoopers.
Hungary maintains its own currency, the Hungarian forint (HUF), although the economy fulfills the Maastricht criteria with the exception of public debt, but it is also significantly below the EU average with the level of 75.3% in 2015. The Hungarian National Bank is currently focusing on price stability with an inflation target of 3%. Hungary's corporate tax rate is only 9%, which is relatively low for EU states.
ENERGY
Hungary's total energy supply is dominated by fossil
fuels, with natural gas occupying the largest share, followed by oil and coal. In June 2020, Hungary passed a law binding itself to a target of
net-zero emissions by 2050. As part of a broader restructuring of the nation's
energy and climate policies, Hungary also extended its National Energy Strategy 2030 to look even further, adding an outlook until 2040 that prioritizes
carbon-neutral and cost-effective energy while focusing on reinforcing energy security and energy independence. Key forces in the country's 2050 target include renewables, nuclear
electricity, and electrification of end-use sectors. Significant investments in the power sector are expected, including for the construction of two new nuclear energy generating units.
Renewable energy capacity has increased significantly, but in recent years growth in the renewables sector has stagnated. What is more, certain policies that limit development of
wind power are expected to negatively impact the
renewables sector.
Hungary's emission of greenhouse gases has dropped alongside the economy's decreasing use of carbon-based fuels. However, independent analysis has identified space for Hungary to set more ambitious emissions reduction targets.
|
Adelaide
Aden
- Yemen
Afghanistan
Africa
Alaska
Albania
Algeria
Amazon
Rainforest
Amsterdam
Antarctic
Arctic
North Pole
Argentina
Asia
Athens
Atlantis
- Plato's Lost City
Australia
Austria
Aztecs
- Mexico
Baghdad
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Beachy
Head, England
Belgium
Benin
Berlin
Bermuda
Black
Rock Desert
Bohemia
Bolivia Bonneville
Utah History
Bonneville,
Utah, USA
Brazil
Brighton
- West Pier
British
Columbia
Buckingham
Palace
Bulgaria
Burkina
Faso
Burma
California
Canada
Canary
Islands
Cape
Horn
Cape
Verde
Cape
York - Au
Caribbean
Cayman
Islands
Central
Africa
Chichester
Harbour
Chile
China
Columbo
- Sri Lanka
Columbia
Corfu
Cowes,
Isle of Wight
Croatia
Crooked
Island, Bahamas
Cuba
Cyprus
Czechoslovakia
Darwin
- Australia
Daytona
Beach
Denmark
Eastbounre
Pier, England
Earthquakes
Ecuador
Egypt
Eindhoven Estonia
Equator
Europe
Falkland
Islands
Falmouth,
Cornwall
Fiji
Finland
France
Galapagos
Islands
Geography
Links
Geography
Mountains
Geography
Records
Geography
Resources
Geography
Statistics
|
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
- Links
Greece
Greenland
Guinea
Guinea
Bissau
Hawaii
Holland
the Nertherlands
Hollywood,
California, LA
Hong
Kong
Hungary
Hurricanes
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Links
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle
of Man
Isle
of Wight
- The
Needles
Israel
Italy
Ivory
Coast
Jakarta
- Java
Japan
Johannesburg
Jordan
Kent,
England
Kenya
Korea
Kuwait
Kyoto
Lanzarote,
Gran Canaria
Las
Vegas
Lebanon
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Life
on Earth
Lithuania
London
- Big
Ben
London
Eye
London
Houses
Parliament
London
- Buckingham
Palace
London
- Old
Bailey
London
- Overview
London
- The City
London
- Tower Bridge
London
- Trafalgar
Square
Luxembourg
Madame
Tussauds
Malaysia
Mali
Malta
Marshal
Islands
Mauritania
Maya
Empire -
Central America
Melbourne,
Australia
Middle
East
Melbourne,
Australia
Mexico
Monaco
Morocco
Mountains
Mumbai
Naples-
Italy
National
Geographic
Nepal
New
York
New
Zealand
Niger
Nigeria
North
Africa
Norway
Nova
Scotia
Oceans
and Seas
Oman
Pakistan
Palermo
- Sicily
Palestine
Palma
- Malorca
|
Panama
Canal - Links
Paris
Pendine
Sands
Peru
Philippines
Pisa,
Leaning Tower
Planet
Earth
Poland
Port
Moresby - PNG
Port
Said - Egypt
Portugal
Puerto
Rico
Qatar
Quebec
Rio
de Janeiro
Romania
Rome
Russia
Salt
Lake City
Samoa
Saudi
Arabia
Scandanavia
Scotland
Senegal
Siera
Leone
Singapore
Solomon
Islands
Somalia
South
Africa
South
America
Southampton
Spain
- Espana
Sri
Lanka - Links
Stonehenge
Sudan
Suez
Canal
Sundancer
Holiday Resort
Sussex,
England Index
Sweden
Switzerland
Sydney,
Australia
Syria
Tahiti
- Polynesia
- Links
Tahitian
- Men & Women Customs
Taiwan
Thailand
The
Gambia
Togo
Tokyo,
Japan
Tonga
- Polynesia
Toronto
Trinidad
- Lesser Antilles
Trinidad
and Tobago
Tsunami
Tunbridge
Wells, England
Tunisia
Turkey
Tuvalu
Islands
UAE
- United Arab Emirates
UK
Statistics
Ukraine
United
Kingdom
United
Kingdom -
Gov
USA
Uruguay
Vanuatu
Islands
Vatican
City
Venezuela
Venice
Vienna
Vietnam
Volcanoes
Volendam
Wales
Washington
D.C.
WAYN
Where Are You Now
Wealden
iron industry
Wendover
West
Africa
World
Peace Supporters
Yemen
Yugoslavia
Zurich
|

Solar
Cola drinkers care about planet
earth
..
Thirst for Life

(330ml
Planet Earth can)
|



