|
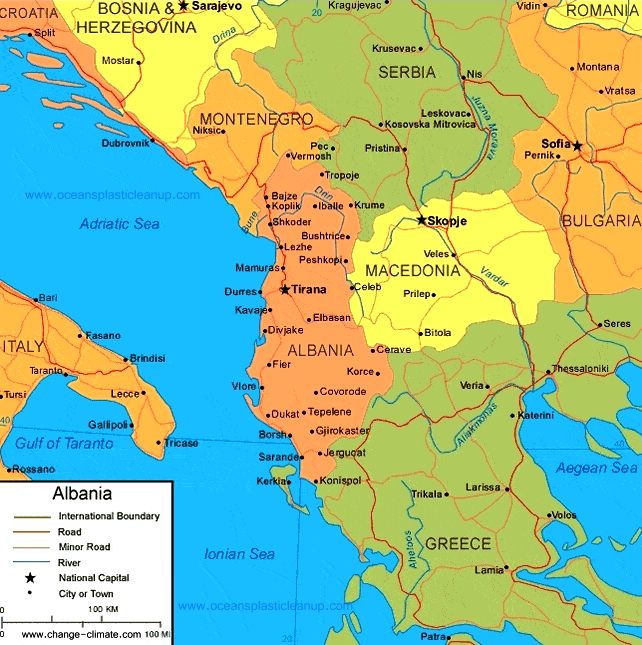
Albania is a country in Southeast
Europe on the
Adriatic
Sea and Ionian Sea within the
Mediterranean
Sea. It shares land borders with Montenegro to the northwest,
Kosovo to the northeast, North Macedonia to the east, Greece to the south and maritime borders with Greece, Montenegro and Italy to the west.
Geographically, the country displays varied climatic, geological, hydrological and morphological conditions, defined in an area of 28,748 km2 (11,100 sq mi). It possesses remarkable diversity with the landscape ranging from the snow-capped mountains in the Albanian Alps as well as the Korab, Skanderbeg, Pindus and Ceraunian Mountains to the hot and sunny coasts of the Albanian Adriatic and
Ionian Sea along the
Mediterranean
Sea.
Historically, the country has been inhabited by numerous civilisations such as the Illyrians, Thracians, Ancient Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, Venetians and Ottomans. The Albanians established the autonomous Principality of Arbėr in the 12th century. The Kingdom of Albania and Principality of Albania has been formed between the 13th and 14th centuries. Prior to the Ottoman conquest of Albania in the 15th century, the Albanian resistance to Ottoman expansion into Europe led by Gjergj Kastrioti Skanderbeg won them acclaim all over most of Europe.
Between the 18th and 19th centuries, Albanians gathered both spiritual and intellectual strength which conclusively led to the Albanian Renaissance. After the defeat of the Ottomans in the Balkan Wars, the modern nation state of Albania emerged in 1912. In the 20th century, the Kingdom of Albania was invaded by Italy which formed Greater Albania before becoming a protectorate of Nazi Germany. Enver Hoxha formed Communist Albania after the
Second World War and launched the Albanians on a path of oppression and decades of isolation. The Revolutions of 1991 concluded the fall of communism in Albania and eventually the establishment of the current Republic of Albania.
Politically, the country is a unitary parliamentary constitutional republic and developing country with an upper-middle income economy dominated by the service sector, followed by manufacturing. It went through a process of transition, following the end of communism in 1990, from centralized planning to a market-based economy. Albania provides universal health care and free primary and secondary education to its citizens.
The country is a member of the United
Nations, World
Bank, UNESCO, NATO, WTO, COE, OSCE and OIC. It is an official candidate for membership in the European Union. It is one of the founding members of the Energy Community, including the Organization of the Black Sea Economic Cooperation and Union for the
Mediterranean.
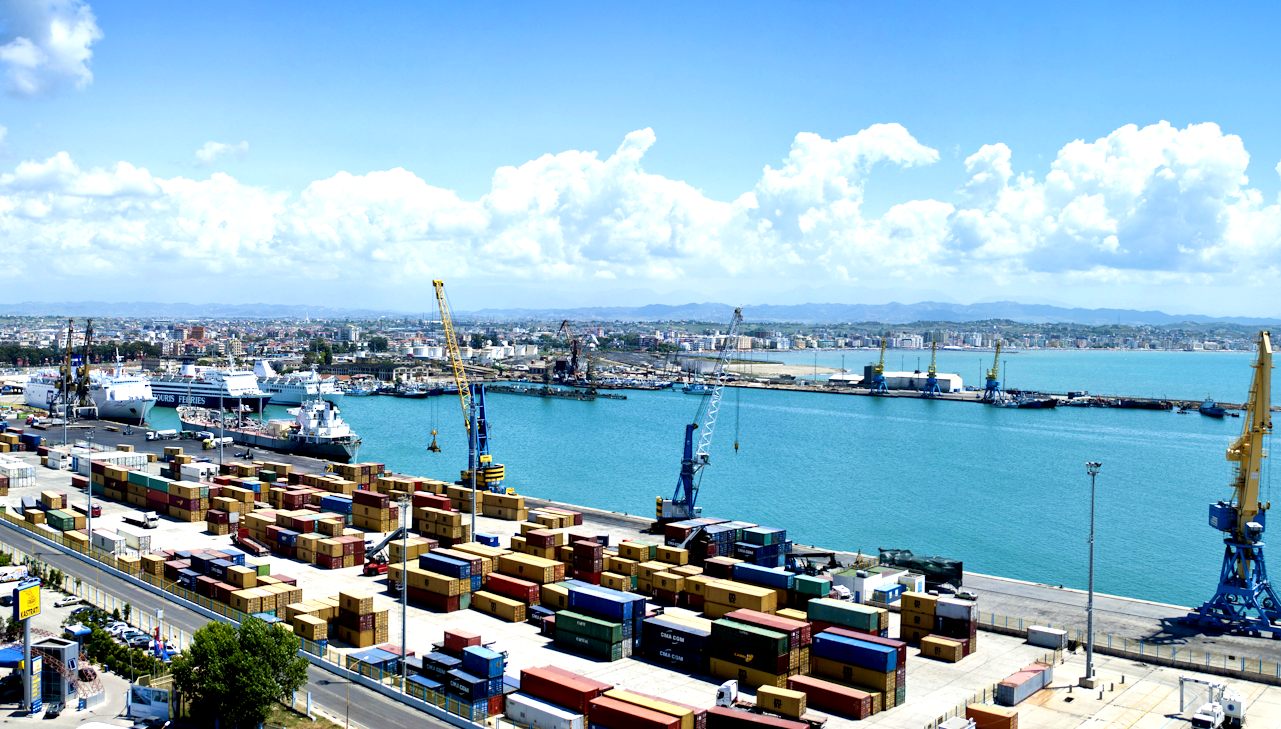

Port
of Durres, Adriatic Sea
ECONOMY
The country has a developing mixed economy classified by the World Bank as an upper-middle income economy. In 2016, it had the 4th lowest unemployment rate in the Balkans with an estimated value of 14.7%. Its largest trading partners are Italy, Greece,
China,
Spain, Kosovo and the
United
States. The lek (ALL) is the country's currency and is pegged at approximately 132,51 lek per euro.
The cities of Tirana and Durrės constitute the economic and financial heart of Albania due to their high population, modern infrastructure and strategic geographical location. The country's most important infrastructure facilities take course through both of the cities, connecting the north to the south as well as the west to the east. Among the largest companies are the
petroleum Taēi Oil, Albpetrol, ARMO and Kastrati, the mineral AlbChrome, the cement Antea, the investment BALFIN Group and the technology Albtelecom, Vodafone, Telekom Albania and others.
In 2012, Albania's GDP per capita stood at 30% of the European Union average, while GDP (PPP) per capita was 35%. Albania were one of three countries in Europe to record an economic growth in the first quarter of 2010 after the global financial crisis. The
International Monetary Fund predicted 2.6% growth for Albania in 2010 and 3.2% in 2011. According to the Forbes as of December 2016, the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) was growing at 2.8%. The country had a trade balance of −9.7% and unemployment rate of 14.7%. The Foreign direct investment has increased significantly in recent years as the government has embarked on an ambitious program to improve the business climate through fiscal and legislative reforms. The economy is expected to expand in the near term, driven by a recovery in consumption and robust investments. Growth is projected to be 3.2% in 2016, 3.5% in 2017, and 3.8% in 2018.

ENERGY
Albania is mostly dependent on hydroelectricity. Almost 94.8% of the country's electricity consumption comes from hydroelectrical stations and ranks 7th in the world by percentage. There are six hydroelectric power stations, including Fierza, Koman, Skavica and Vau i Dejės situated within the Drin River. Further, there are two stations under construction, namely Banjė and Moglicė located in the Devoll River. Both are expected to be completed between 2016 and 2018.
Albania has considerably large deposits of oil. It has the 10th largest oil reserves in europe and the 58th in the world. The country's main
petroleum deposits are located around the Albanian Adriatic Sea Coast and Myzeqe Plain within the Western Lowlands, where the country's largest reserve is located. Although, Patos-Marinza, also located within the area, is the largest onshore oil field in Europe.
In 2015, 498 kilometres (309 mi) of natural gas pipelines and 249 kilometres (155 mi) of oil pipelines spanned the country's territory. The planned Trans Adriatic Pipeline, a major trans Adriatic Sea
gas pipeline, will delivers natural gas from Azerbaijan to Albania and Western Europe through Italy and will be completed in 2020.
Further, Albania and Croatia have discussed the possibility of jointly building a
nuclear power plant at Lake Shkodėr, close to the border with Montenegro, a plan that has gathered criticism from Montenegro due to seismicity in the area. In 2009, the company Enel announced plans to build an 800 MW
coal-fired power plant in the country, to diversify
electricity sources.

TRANSPORT
Transportation in Albania has undergone significant changes and improvements in the past two decades. Continual improvements to the public transport, road and rail infrastructure,
water and
air travel have all led to a vast enhancement in transportation.
The international airport of Tirana serves as the premier gateway to the country and carries almost 2.5 million passengers per year with connections to many destinations in other countries around Europe. The country plans to progressively increase the number of airports especially in the south with possible locations in Sarandė, Gjirokastėr and Vlorė.
The highways and motorways in Albania are properly maintained and often still under construction. The A1 represents a major transportation corridor in Albania and the longest motorway of the country. It will prospectively link Durrės on the Adriatic Sea across Pristina in Kosovo with the Pan-European Corridor X in Serbia. The A2 is part of the AdriaticIonian Corridor as well as the Pan-European Corridor VIII and connects Fier with Vlorė. The A3 is currently under construction and will connect, after its completion, Tirana and Elbasan with the Pan-European Corridor VIII. When all three corridors are completed, Albania will have an estimated 759 kilometres (472 mi) of highway linking it with all of its neighboring countries.
Durrės is the busiest and largest seaport in the country followed by Vlorė, Shėngjin and Sarandė. As of 2014, it is as one of the largest passenger ports on the Adriatic Sea with annual passenger volume of approximately 1.5 million. The principal ports serve a system of ferries connecting numerous islands and coastal cities in Croatia, Greece and
Italy.
The rail network is administered by the national railway company Hekurudha Shqiptare which was extensively promoted by the dictator Enver Hoxha. There has been a considerable increase in private car ownership and bus usage while rail use decreased since the end of communism. However, a new railway line from Tirana and its airport to Durrės is currently planned. The specific location of this railway, connecting the most
populated urban areas in Albania, merely makes it an important economic development project.

LINKS
& REFERENCE
http://
|
Adelaide
Aden
- Yemen
Afghanistan
Africa
Alaska
Albania
Algeria
Amazon
Rainforest
Amsterdam
Antarctic
Arctic
North Pole
Argentina
Asia
Athens
Atlantis
- Plato's Lost City
Australia
Austria
Aztecs
- Mexico
Baghdad
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Beachy
Head, England
Belgium
Benin
Berlin
Bermuda
Black
Rock Desert
Bohemia
Bolivia Bonneville
Utah History
Bonneville,
Utah, USA
Brazil
Brighton
- West Pier
British
Columbia
Buckingham
Palace
Bulgaria
Burkina
Faso
Burma
California
Canada
Canary
Islands
Cape
Horn
Cape
Verde
Cape
York - Au
Caribbean
Cayman
Islands
Central
Africa
Chichester
Harbour
Chile
China
Columbo
- Sri Lanka
Columbia
Corfu
Cowes,
Isle of Wight
Croatia
Crooked
Island, Bahamas
Cuba
Cyprus
Czechoslovakia
Darwin
- Australia
Daytona
Beach
Denmark
Eastbounre
Pier, England
Earthquakes
Ecuador
Egypt
Eindhoven Estonia
Equator
Europe
Falkland
Islands
Falmouth,
Cornwall
Fiji
Finland
France
Galapagos
Islands
Geography
Links
Geography
Mountains
Geography
Records
Geography
Resources
Geography
Statistics
|
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
- Links
Greece
Greenland
Guinea
Guinea
Bissau
Hawaii
Holland
the Nertherlands
Hollywood,
California, LA
Hong
Kong
Hungary
Hurricanes
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Links
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle
of Man
Isle
of Wight
- The
Needles
Israel
Italy
Ivory
Coast
Jakarta
- Java
Japan
Johannesburg
Jordan
Kent,
England
Kenya
Korea
Kuwait
Kyoto
Lanzarote,
Gran Canaria
Las
Vegas
Lebanon
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Life
on Earth
Lithuania
London
- Big
Ben
London
Eye
London
Houses
Parliament
London
- Buckingham
Palace
London
- Old
Bailey
London
- Overview
London
- The City
London
- Tower Bridge
London
- Trafalgar
Square
Luxembourg
Madame
Tussauds
Malaysia
Mali
Malta
Marshal
Islands
Mauritania
Maya
Empire -
Central America
Melbourne,
Australia
Middle
East
Melbourne,
Australia
Mexico
Monaco
Morocco
Mountains
Mumbai
Naples-
Italy
National
Geographic
Nepal
New
York
New
Zealand
Niger
Nigeria
North
Africa
Norway
Nova
Scotia
Oceans
and Seas
Oman
Pakistan
Palermo
- Sicily
Palestine
Palma
- Malorca
|
Panama
Canal - Links
Paris
Pendine
Sands
Peru
Philippines
Pisa,
Leaning Tower
Planet
Earth
Poland
Port
Moresby - PNG
Port
Said - Egypt
Portugal
Puerto
Rico
Qatar
Quebec
Rio
de Janeiro
Romania
Rome
Russia
Salt
Lake City
Samoa
Saudi
Arabia
Scandanavia
Scotland
Senegal
Siera
Leone
Singapore
Solomon
Islands
Somalia
South
Africa
South
America
Southampton
Spain
- Espana
Sri
Lanka - Links
Stonehenge
Sudan
Suez
Canal
Sundancer
Holiday Resort
Sussex,
England Index
Sweden
Switzerland
Sydney,
Australia
Syria
Tahiti
- Polynesia
- Links
Tahitian
- Men & Women Customs
Taiwan
Thailand
The
Gambia
Togo
Tokyo,
Japan
Tonga
- Polynesia
Toronto
Trinidad
- Lesser Antilles
Trinidad
and Tobago
Tsunami
Tunbridge
Wells, England
Tunisia
Turkey
Tuvalu
Islands
UAE
- United Arab Emirates
UK
Statistics
Ukraine
United
Kingdom
United
Kingdom -
Gov
USA
Uruguay
Vanuatu
Islands
Vatican
City
Venezuela
Venice
Vienna
Vietnam
Volcanoes
Volendam
Wales
Washington
D.C.
WAYN
Where Are You Now
Wealden
iron industry
Wendover
West
Africa
World
Peace Supporters
Yemen
Yugoslavia
Zurich
|

Solar
Cola drinkers care about planet
earth
..
Thirst for Life

(330ml
Planet Earth can)
|



